Search Results for: surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension The expression of intermolecular attraction at the surface of a liquid, in contact with air or another gas,... Read More
Abiotic Factors – Water Conditions
Evidently, the light and heat from the sun play an important role in providing suitable conditions. However, the water... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Capillary action
Definition noun The movement of a liquid, e.g. water molecules, through a narrow space as a result of cohesion, adhesion,... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
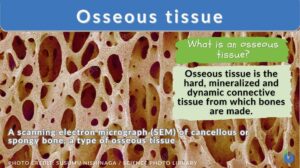
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Alveolar cell
Definition noun, plural: alveolar cells The cell lining the pulmonary alveolus; the cell of the air sac of the... Read More
Water potential
Definition noun The measure of the relative tendency of water to move from one area to another, and is commonly represented... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Hydrogen bond
Definition noun plural: hydrogen bonds A type of chemical bond that is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Microfilament
Definition noun plural: microfilaments mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī'krō-fil'ă-mĕnts A thin, helical, single-stranded... Read More
Epithelium
An epithelium is a type of animal tissue made up of densely packed cells (called epithelial cells) that rest on a basement... Read More